Neo4j Versioner SQL Documentation
Neo4j Versioner SQL is a collection of procedures, aimed to help developers to manage a SQL Database schema, through the Entity-State model applied to Neo4j.
License
Apache License 2.0
Installation
- Neo4j Versioner Core is required, please see the current documentation here;
- Download the latest release;
- Put the downloaded jar file into
$NEO4J_HOME/pluginsfolder; - Put your database JDBC driver into
$NEO4J_HOME/pluginsfolder, for more information on supported databases, click here; - Start/Restart Neo4j.
About
Neo4j Versioner SQL has been developed by Alberto D’Este and Marco Falcier.
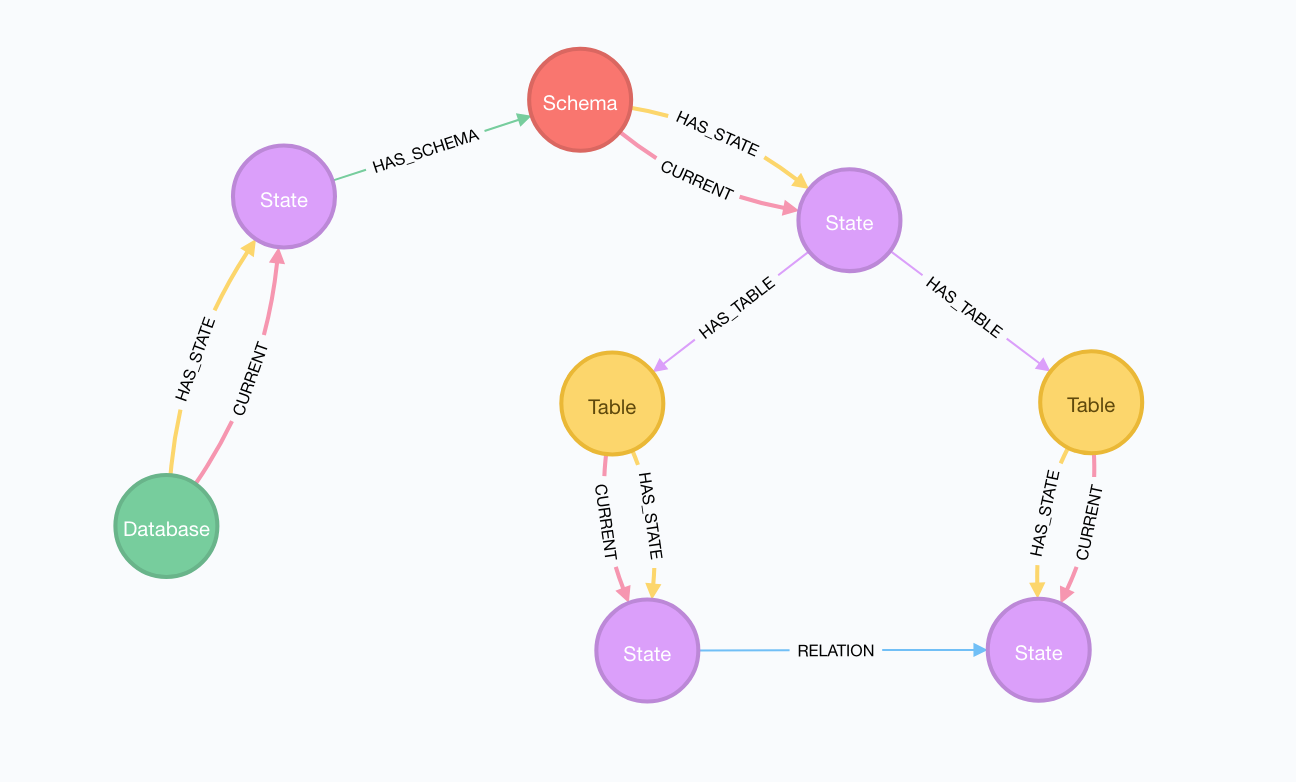
Data Model
The current data model is a hierarchical representation of the database, that recursively uses the Core entity-state model. Entity nodes are:
Database: it has a type (postgres, mysql, …) and a name properties;Schema: it has a name property;Table: it has a name property.
Every Entity has its own State nodes: in Table’s State node we can find all columns name as keys, and their properties as values, for example
id: int
name: varchar
Table’s State nodes can be connected together by the RELATION relationship, which mean that one of the two connected Table’s State node, has at least one foreign key to another Table’s State node.
Every State node, with its RELATION relationship is a snapshot of the current structure of the SQL database.
There are 3 different relationships, in addition to the Core ones:
(:Database)--(:State)-[:HAS_SCHEMA]->(:Schema)(:Schema)--(:State)-[:HAS_TABLE]->(:Table)(:Table)--(:State)-[:RELATION {destination_column: id, source_column: external_id, constraint: external_id}]->(:State)--(:Table): it contains the foreign key information.
This is how the data model looks like:
Currently supported databases
postgresmysql
Procedures Reference
Neo4j procedure documentation can also be found using CALL dbms.procedures().
Procedure CheatSheet
Here you can find a “compressed” list of all the procedures:
Legend
- Optional parameter
- Node/Path
| name | parameters | return values | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sql.versioner.init | dbname, hostname, port, database, username, password | node | Initialize a Database Version with its schemas, tables and relative columns. |
| sql.versioner.reload | hostname, port, username, password | node | Reload a new Database Version with its schemas, tables and relative columns. |
init
This procedure is used in order to initialize a Database Version with its schemas, tables and relative columns. It will create a graph as showed in the data model section.
Details
Name
sql.versioner.init
Parameters
| name | necessity | detail |
|---|---|---|
dbname |
mandatory | The name of the database type you are going to import; see supported databases. |
hostname |
mandatory | The database hostname. |
port |
mandatory | The database port. |
database |
mandatory | The database name you are going to import. |
username |
mandatory | The username for connecting to the given database. |
password |
mandatory | The username’s password. |
Return value
| name | type |
|---|---|
| node | Node |
Example call
CALL sql.versioner.init('mysql', 'localhost', 3306, 'new_schema', 'root', 'password') YIELD node return node
reload
This procedure is used in order to reload a new Database Version with its schemas, tables and relative columns.
It will create a new State for every entity change, if needed.
Details
Name
graph.versioner.init
Parameters
| name | necessity | detail |
|---|---|---|
hostname |
mandatory | The database hostname. |
port |
mandatory | The database port. |
username |
mandatory | The username for connecting to the given database. |
password |
mandatory | The username’s password. |
Return value
| name | type |
|---|---|
| node | Node |
Example call
CALL sql.versioner.reload('localhost', 3306, 'root', 'password') YIELD node return node
Feedback
We would appreciate your feedback about our Versioner SQL, how to improve and fix (we hope not so many!) any bad things. Say yours in the issue section.